EV Charger Overload Protection Failure: Common Causes, Identification, and Prevention Strategies
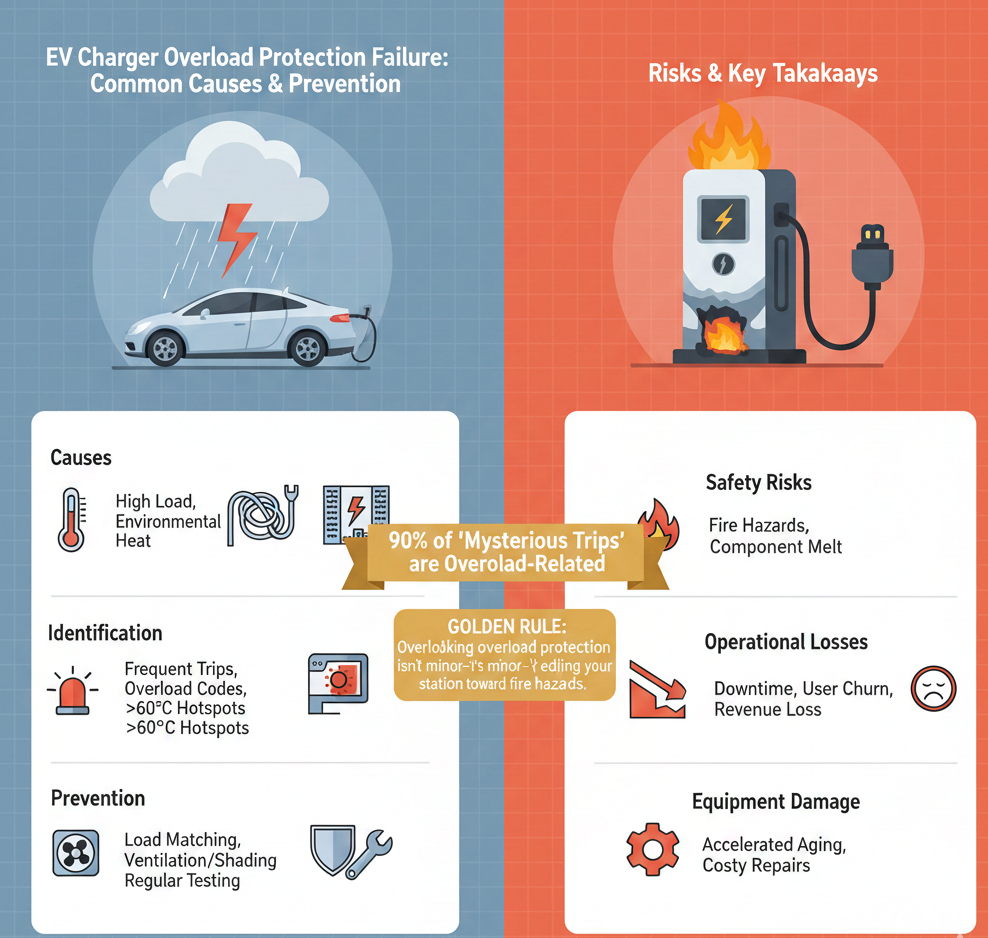
Ever experienced your EV charger suddenly tripping, showing an “Overload” error, or shutting down during operation? Based on real feedback from installers and operators, 90% of such interruptions stem from the overload protection mechanism being triggered incorrectly or failing, rather than a core equipment fault. This is especially common in high-load scenarios, rainy outdoor setups, or older grids (a frequent issue in the Netherlands). This article draws from actual project experiences to break down the causes and solutions, helping you avoid safety risks and operational downtime.
What Is EV Charger Overload Protection Failure? Overload protection failure occurs when the charger’s built-in overcurrent or thermal protection (per IEC 61851) does not respond correctly or triggers too often, interrupting normal charging. Common triggers include sustained high power output, environmental overheating, cable issues, or grid instability. Typical client complaint: “It trips after a few minutes at full load” – often due to heat buildup or current exceeding safe limits without proper cutoff.
How to Identify Overload Protection Issues? Key on-site checks:
- Frequent tripping / error codes: Overload indicator lights up or displays “Overcurrent / Overload”.
- Abnormal temperature: Charger body or cables >60–70°C (use thermal imaging to spot hotspots).
- False triggering: Protection activates under normal load or fails to reset easily.
| Issue Type | Identification Signal | Common Client Complaints |
|---|---|---|
| Frequent False Trips | Trips at normal power, error code Overload | “Stops charging right after starting” |
| Thermal Protection Failure | Device overheats without power reduction | “Gets very hot in summer but keeps running” |
| Overcurrent Not Responding | Current exceeds limit but no cutoff | “Sudden short circuit after full load” |
| Environment Amplification | Worse in rain / poor ventilation | “Outdoor unit trips often in wet weather” |
How to Prevent and Correct Overload Protection Issues?
Follow IEC 61851 (Mode 3 requires overcurrent and thermal protection) and local EU/Netherlands regulations:
- Load Matching: Ensure grid and cables support peak power without overload.
- Heat Management: Maintain >50 cm clearance around the unit; add shading or waterproof covers (essential for Dutch rainy seasons).
- Regular Testing: Simulate full-load operation every 6 months and verify protection response time.
- Enhanced Protection: Install Type B RCD or additional temperature sensors that reduce power when >85°C is detected.
Potential Risks of Overload Protection Failure. Ignoring these issues can lead to:
- Safety incidents: Overheating can melt components or cause fires (EU data links 15–20% of failures to overload-related causes).
- Operational downtime: Frequent interruptions lead to customer loss and revenue impact.
- Equipment damage: Prolonged overload accelerates wear on electronics, increasing repair costs.
FAQ
- Q: Why does overload protection trigger so often?
- A: Usually due to high voltage drop in cables, poor ventilation, or mismatched load – check cable sizing and environment first.
- Q: How to protect outdoor chargers in the Netherlands?
- A: Prioritize ventilation, thermal monitoring, and IP65 rating with shading for rainy seasons.
Feel free to share your overload protection experiences.
